

For servers to automatically enroll and stop generating and using self-signed certificates a GPO must be configured. Publish the new RDP template to a certificate authority. On the Security tab set Read and Enroll for targeted servers or In the Object Identifier field (delete the default value in the box) then OK Now click Add and the Add Application Policyīox opens select New and in the New Application Policy dialog box enter The Extensions tab and select Application Polices and click Edit. Then right click on the default Computer template and duplicate template. To create the policy, open certificate templates console ( certtmpl.msc) The highlighted policy above is Microsoft’s OID designationįor Remote Desktop Authentication (1.3.6.1.4.1.311.54.1.2) but isn’t present by OID(s) that start with 1.3.6.1.4.1.311 are Microsoft based policies Upon the first RDP connection, servers and clients generate a self-signed certificate, which are not trusted so the warning is displayed. The most noticeable is the warning displayed when making an RDP connection to a server or client.

There are multiple reasons to issue RDP certificates from a PKI.
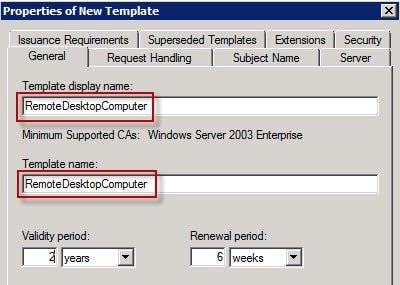
A best practice I always follow is no spaces in template names and setting template name and template display name to match when possible. Pay close attention to this if there are server OS(s) below Windows Server 2012 in your environment and use template name or OID when specifying the RDP template. At each subsequent GPO refresh the process was repeated resulting in huge numbers of RDP certificates being issued. Prior to Windows Server 2012, a bug existed where using the template Display Name in the GPO (below), would trigger an enrollment, however the policy would not honor it. In this blog, I will show how to create the template, why the OID and extensions are important, and how to implement it and remove self-signed certificate warnings In a previous blog on Object Identifiers (OID) in PKI, I mentioned creating a certificate template for Remote Desktop Connection (RDP).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
